SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS
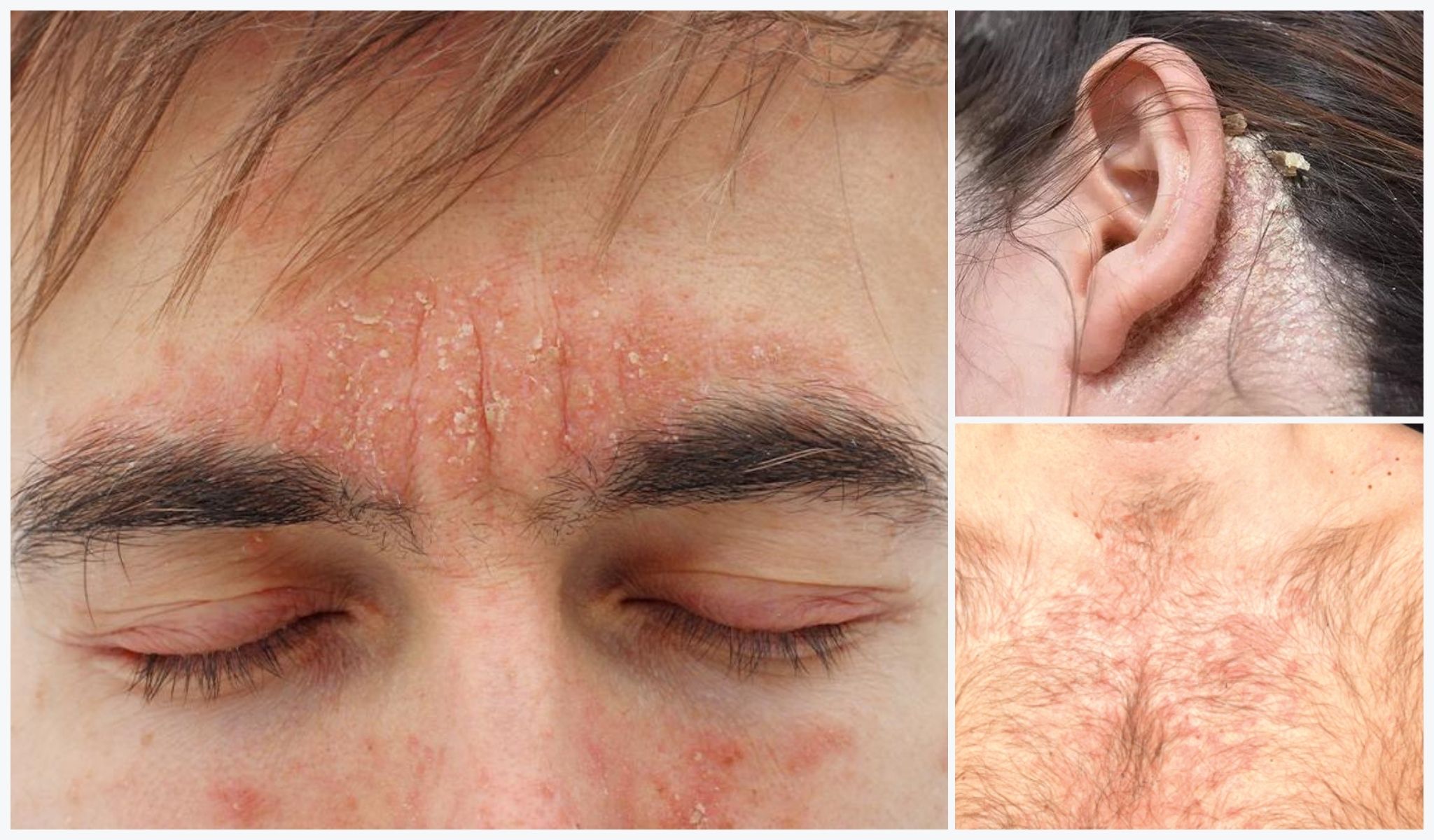
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic skin condition that primarily affects the scalp, but it can also occur on other parts of the body where there are a significant number of oil glands. This condition is characterized by red, scaly, and sometimes itchy patches on the skin. It often appears as dandruff on the scalp, but it can also affect the face, ears, chest, back, and other areas with high oil gland activity.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis:
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development, including:
- Malassezia yeast: This type of yeast is normally present on the skin’s surface but can overgrow in some individuals, leading to skin irritation and inflammation.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic predisposition to seborrheic dermatitis, as it tends to run in families.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, or with certain medical conditions, can trigger or worsen seborrheic dermatitis.
- Stress: High levels of stress can exacerbate the condition.
- Weather conditions: Cold, dry weather or excessive heat and humidity can trigger or worsen symptoms in some people.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis
The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Redness and inflammation of affected areas.
- Greasy or oily appearance of the skin or scalp.
- Flaky, white or yellow scales on the scalp (dandruff).
- Itching or burning sensations.
- Crusting and oozing in severe cases.
How to manage Seborrheic Dermatitis?
While seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition, it can often be managed with various treatments, including:
- Medicated shampoos: Over-the-counter or prescription shampoos containing active ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or coal tar can help control scalp symptoms.
- Topical creams and ointments: Prescription-strength topical treatments containing corticosteroids or antifungal agents may be recommended for more severe cases or when other areas of the body are affected.
- Antifungal medications: In cases where yeast overgrowth is a significant factor, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding triggers such as excessive stress, harsh skincare products, and extreme weather conditions can help manage symptoms.
It’s essential to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan if you suspect you have seborrheic dermatitis. While the condition is not curable, it can usually be effectively controlled with appropriate care and treatment.
