FUNGAL INFECTIONS
What is Fungal Infection?
Dermatological fungal infections, also known as dermatophytosis or tinea infections, are fungal infections that affect the skin, hair, and nails. These infections are caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes.
Dermatophytes feed on keratin and thrive in warm, moist environments. These infections are quite common and can affect people of all ages.
Types of Skin Fungal Infection?
There are several types of dermatological fungal infections, which are classified based on the location and characteristics of the infection. Some common types include:
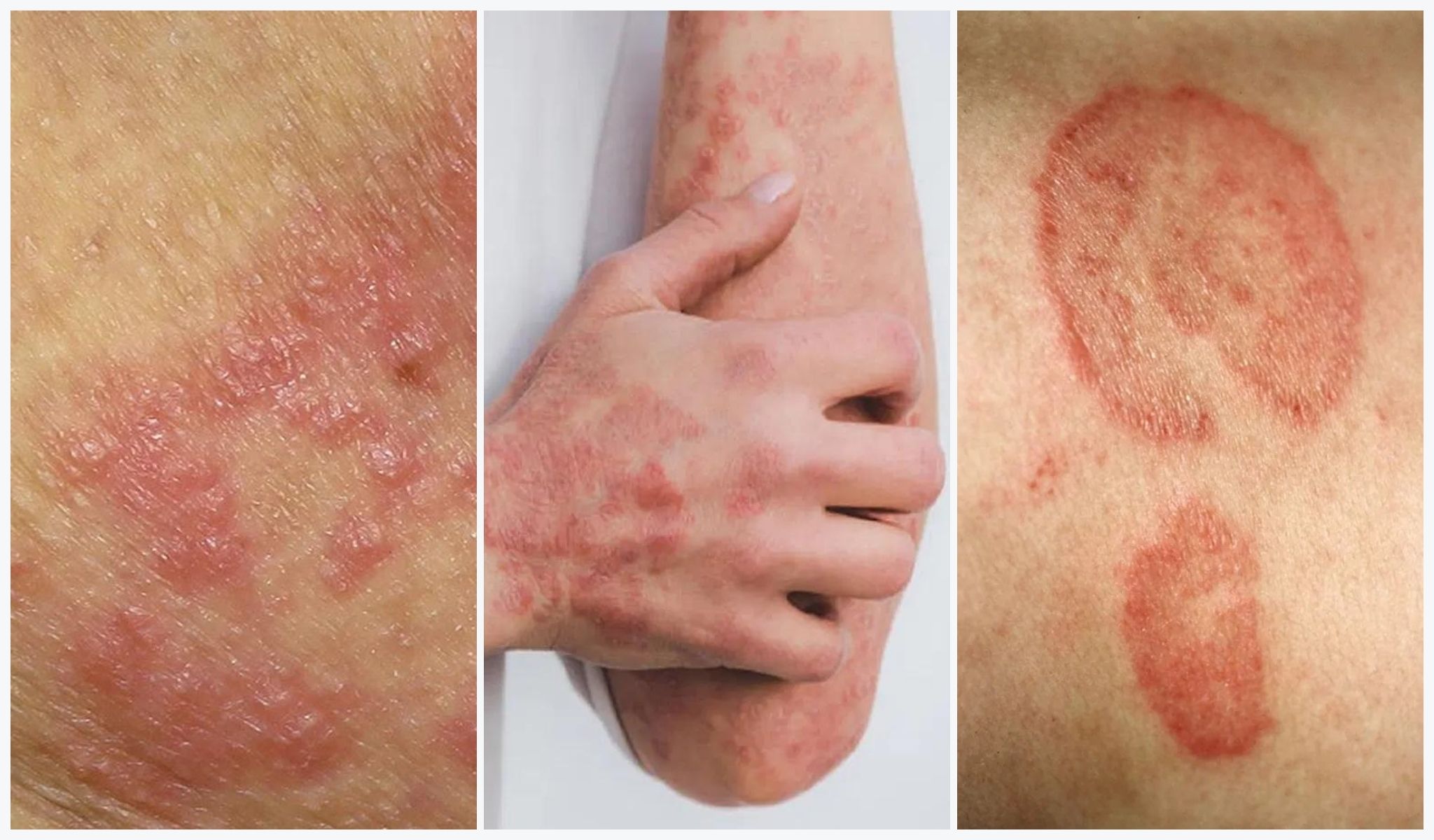
- Tinea Corporis (Ringworm): Affects the body and typically appears as a red, circular rash with a raised, scaly border.
- Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot): Affects the feet, causing itching, peeling, and redness, often between the toes.
- Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch): Affects the groin area and is characterized by a red, itchy rash.
- Tinea Capitis: Affects the scalp and hair, often leading to hair loss and scaling of the skin.
- Tinea Unguium (Onychomycosis): Affects the nails, causing them to become thickened, discolored, and brittle.
Causes of Dermatological Fungal Infection
Dermatophytes are typically transmitted from person to person or from animals to humans. The common causes of dermatological fungal infections include:
- Direct Contact: The most common mode of transmission is direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or animal
- Indirect Contact: Fungi can also survive on contaminated objects such as combs, brushes, bedding, or clothing, leading to infection when these items come into contact with the skin.
- Environmental Factors: Walking barefoot in damp or humid environments, such as communal showers, locker rooms, or swimming pools, can expose individuals to fungal spores.
How to treat Dermatological Fungal Infections?
The treatment of dermatological fungal infections typically involves antifungal medications, which can be either topical (applied to the skin) or oral (taken by mouth). The choice of treatment depends on the severity and location of the infection.
- Topical Antifungals: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, or powders are often effective for mild cases. Prescription-strength topical medications may be necessary for more severe infections.
- Oral Antifungals: When the infection is widespread or involves the nails, oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine or itraconazole may be prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Treating Recurrent Infections: Some individuals are more prone to fungal infections. If you experience recurrent infections, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and preventive measures.
How to prevent the spread of Fungal Infections ?
Preventing fungal infections involves adopting various measures to reduce the risk of fungal growth and transmission. Here are few preventive strategies:
- Maintain good hygiene.
- Keeping the affected area clean and dry is important for preventing the spread of the infection and aiding in recovery.
- Sharing Personal Items Towels, clothing, or sports equipment.
- Avoid Prolonged exposure to moisture.
- Wear breathable clothing.
- Avoiding Irritating Substances that can worsen the condition, such as perfumed soaps, tight clothing, or excessive sweating.
- Practice good skincare, nail and foot care.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas
If you suspect you have a fungal infection or have persistent symptoms, it’s essential to seek dermatologist’s advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
