DERMATITIS
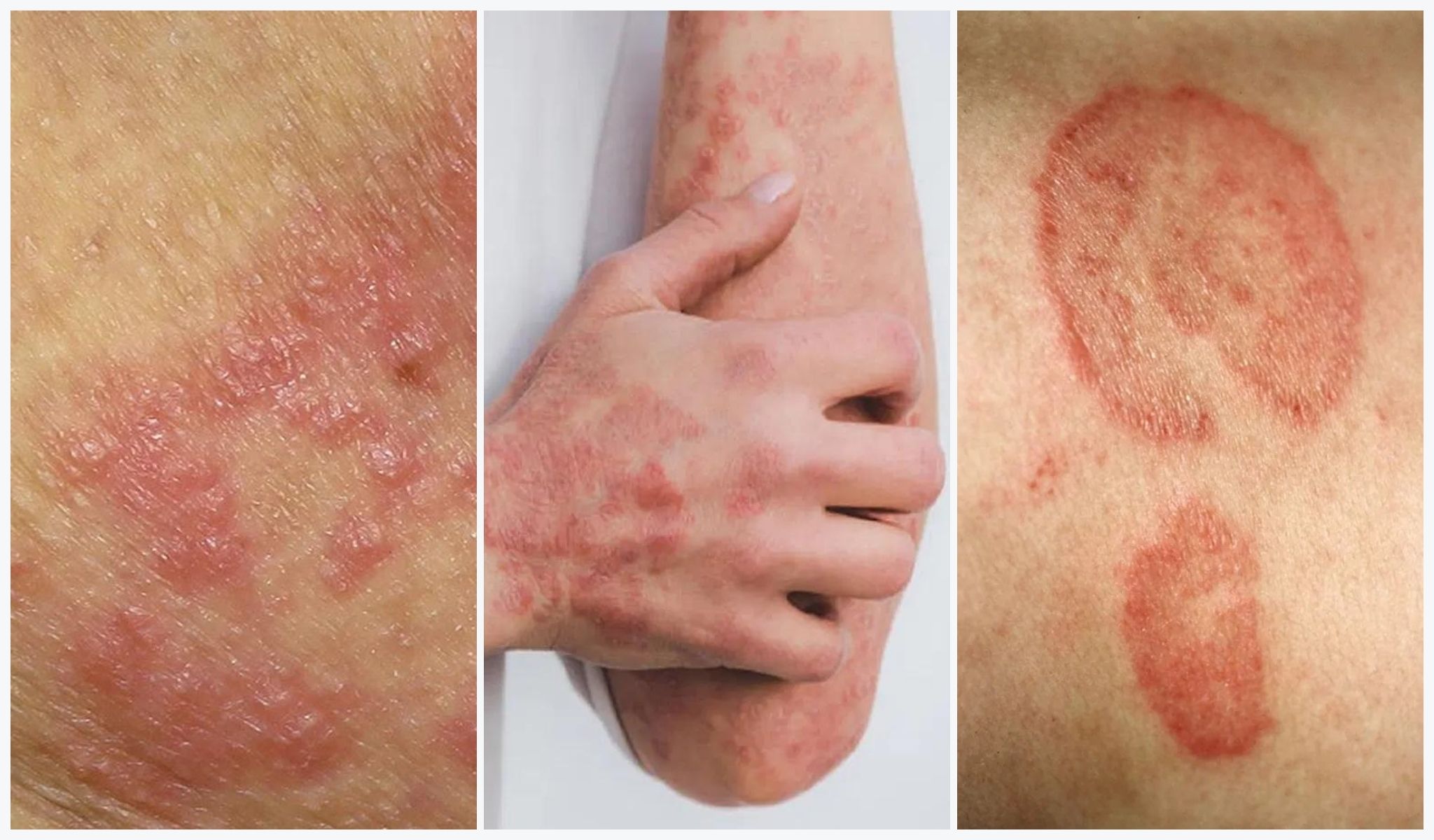
What is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, itching, and the formation of dry, scaly, or oozing rashes on the skin.
Types of Dermatitis
Specific type of dermatitis depends on the underlying trigger or irritant. Some common types of dermatitis include:
- Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin comes into contact with irritants or allergens. There are two main types:
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Caused by exposure to substances that directly damage or irritate the skin, such as chemicals, soaps, or detergents.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by an allergic reaction to specific substances, such as certain metals (e.g., nickel), cosmetics, or plants like poison ivy.
- Atopic Dermatitis : Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often runs in families and is associated with a genetic predisposition to allergies and asthma.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This type of dermatitis primarily affects areas of the skin rich in sebaceous (oil) glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. It can lead to flaky, greasy, and red skin, often referred to as dandruff when it affects the scalp.
- Nummular Dermatitis: This type of dermatitis is characterized by coin-shaped patches of red, itchy skin. It often appears after skin injuries, such as insect bites or abrasions.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Typically occurring in the lower legs, stasis dermatitis is associated with poor blood circulation in the veins, leading to swelling, redness, and skin changes.
- Perioral Dermatitis: This type of dermatitis primarily affects the skin around the mouth and can appear as red, bumpy, or pimple-like rashes.
- Dyshidrotic Dermatitis: Also known as pompholyx, this type of dermatitis involves the formation of small, itchy blisters on the palms, fingers, or soles of the feet.
Symptoms of Dermatitis
There are several types of dermatitis, each with its own set of symptoms. However, common symptoms of dermatitis can include:
- Redness: The affected skin often appears red or pink due to inflammation.
- Itching: Itchiness is a hallmark symptom of dermatitis. The severity of itching can range from mild to intense and can significantly disrupt daily activities and sleep.
- Rash: Dermatitis typically causes a rash, which can take various forms.
- Eczematous Rash: Characterized by redness, swelling, and small fluid-filled blisters (vesicles).
- Papules: Small raised bumps on the skin.
- Hives (urticaria): Raised, itchy welts with defined borders.
- Scales or flakes: Dry, scaly patches of skin.
- Dryness: Affected skin often feels dry, rough, and may become cracked or scaly.
- Swelling: Inflammation can lead to swelling or puffiness of the affected skin.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some forms of dermatitis can cause pain or discomfort, particularly when the skin is cracked or open.
- Burning or Stinging: In addition to itching, the skin may feel like it’s burning or stinging.
- Weeping or Oozing: In severe cases, dermatitis can lead to the oozing of clear or yellowish fluid from the affected areas.
- Thickened Skin (Lichenification): Chronic or untreated dermatitis can lead to thickening and hardening of the skin in the affected areas.
- Skin Color Changes: Over time, the skin may become darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation) than the surrounding skin.
The specific symptoms and appearance of dermatitis can vary depending on the type of dermatitis, its cause, and the individual’s skin type. If you have persistent or severe dermatitis, consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. They can provide guidance on managing your specific type of dermatitis.
How to prevent from Dermatitis?
Preventing dermatitis involves taking steps to protect your skin from irritants and allergens that can trigger this condition. Here are some practical tips to help you prevent dermatitis:
- Identify Triggers: Understand what substances or conditions cause your dermatitis. Common triggers include soaps, detergents, certain fabrics, chemicals, and specific foods. Identifying your triggers is the first step in prevention.
- Choose Skin-Friendly Products:
- Use mild, fragrance-free soaps and detergents.
- Opt for hypoallergenic and non-comedogenic skincare and cosmetic products.
- Avoid products with harsh chemicals, preservatives, or fragrances.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keep your skin well-hydrated by applying a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer after bathing and as needed throughout the day. Choose moisturizers that contain ceramides or humectants like glycerin to help repair the skin’s natural barrier.
- Protect Your Skin: Wear protective clothing, such as gloves and long-sleeved shirts, when working with chemicals or irritants. Use barrier creams or ointments on exposed skin before activities that may irritate the skin.
- Practice Proper Hand Hygiene:
- Wash your hands with mild soap and warm water.
- Avoid excessive hand-washing or using hot water, which can strip away natural oils.
- Moisturize your hands after washing.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Cold, dry air can worsen dermatitis. Use a humidifier to add moisture to indoor air during the winter months. In hot weather, wear breathable, loose-fitting clothing to minimize sweating and irritation.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate dermatitis symptoms. Practice stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Dietary Considerations: If you suspect food allergies are contributing to your dermatitis, consult an allergist for testing and dietary recommendations. Maintain a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids to support overall skin health.Stay
- Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated from the inside out.
- Allergen Avoidance: If you have contact dermatitis, identify and avoid allergens by reading product labels carefully. Consider patch testing by a dermatologist to pinpoint specific allergens.
