BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
What is Bacterial Infection?
A skin bacterial infection is a condition in which harmful bacteria invade and multiply within the skin, leading to various symptoms and skin-related issues. These infections can occur on any part of the body and may range from mild to severe.
Types of Skin Bacterial Infection
Common types of skin bacterial infections include:
- Cellulitis: Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection typically caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria. Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body and often requires antibiotic treatment.
- Impetigo: Impetigo is a highly contagious skin infection caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria. It is more common in children and is characterized by the development of red sores or blisters that can burst and form a honey-colored crust.
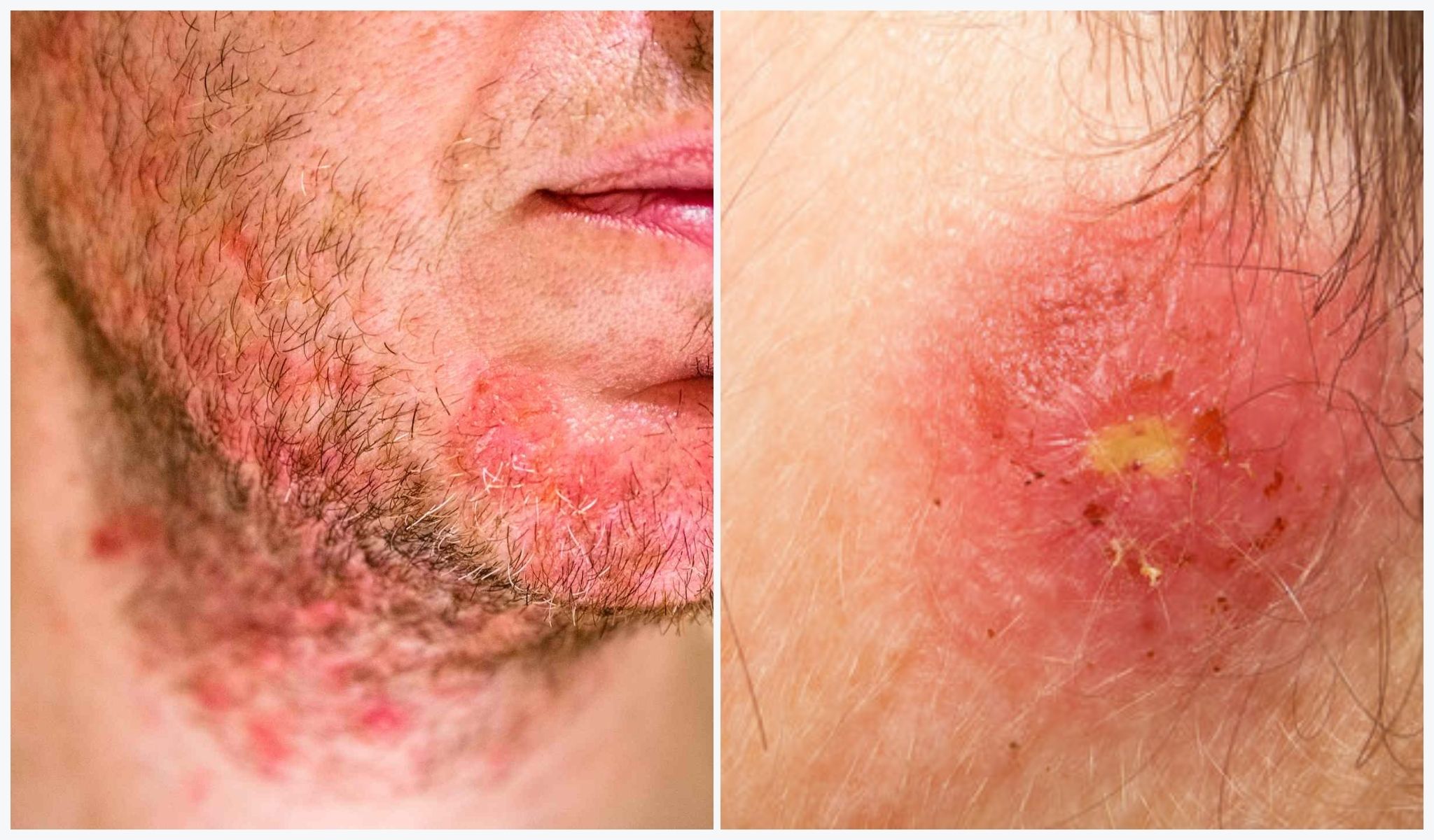
- Folliculitis: Folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become infected, often due to Staphylococcus bacteria. It can result in red, pus-filled bumps around hair follicles, resembling pimples.
- Boils (Furuncles and Carbuncles): Boils are painful, pus-filled lumps that form when hair follicles become infected with Staphylococcus bacteria. Furuncles are single boils, while carbuncles are collections of boils clustered together.
- Abscesses: An abscess is a localized collection of pus within a cavity formed by the body’s response to infection. Abscesses can occur anywhere on the body and often require drainage and antibiotic treatment.
- Erysipelas: Erysipelas is a superficial skin infection typically caused by Streptococcus bacteria. It presents as a red, swollen, and painful rash with well-defined borders.
- Pitted Keratolysis: Pitted keratolysis is a bacterial infection of the soles of the feet characterized by small, shallow pits or depressions in the skin. It’s caused by specific bacteria that thrive in moist conditions.
- Leprosy (Hansen’s Disease): Leprosy is a chronic bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin and peripheral nerves, leading to skin lesions, nerve damage, and deformities if left untreated.
Symptoms of Dermatological Bacterial Infection
Here’s a closer look at the symptoms of skin bacterial infections and how they can spread:
- Redness: Infected areas often become red due to inflammation caused by the body’s immune response to the bacteria.
- Swelling: Inflammation can lead to swelling as blood vessels dilate and fluid accumulates in the affected area.
- Warmth: The infected area might feel warm to the touch due to increased blood flow and inflammation.
- Pain or Tenderness: Bacterial infections can cause pain or tenderness at the site of infection.
- Pus Formation: Pus-filled blisters, pustules, or abscesses can develop, especially in cases of more severe infections.
- Itching or Burning: Skin infections can cause itching, burning, or discomfort in the affected area.
- Crusting or Scaling: Some infections can lead to crusting, scaling, or oozing of the skin.
- Fever: Systemic symptoms like fever may be present if the infection is severe or has spread beyond the skin.
What can cause Skin Bacterial Infection?
Skin bacterial infections are typically caused by the invasion and multiplication of harmful bacteria on or within the skin. Several factors can contribute to the development of these infections:
- Bacteria: Various types of bacteria can cause skin infections. The most common culprits include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus), and, in the case of leprosy, Mycobacterium leprae.
- Breaks in the Skin: One of the most common ways bacteria enter the skin is through breaks or damage to the skin’s protective barrier. This can include cuts, scrapes, insect bites, surgical incisions, or even conditions like eczema or dermatitis, which can compromise the skin’s integrity.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate personal hygiene can create an environment where bacteria thrive. Accumulation of sweat, dirt, or oils on the skin can provide a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Contaminated Objects: Bacteria can be transferred from contaminated objects or surfaces to the skin. Sharing personal items like towels, razors, or clothing can facilitate the spread of bacteria.
- Close Skin Contact: Skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, especially in situations where there is friction or moisture, can transfer bacteria from one person to another.
- Insect Bites and Stings: Some skin infections, like cellulitis, can occur when bacteria enter the skin through insect bites or stings.
- Chronic Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or conditions that weaken the immune system, can make individuals more susceptible to skin infections.
How to prevent the spread of Bacterial Infections ?
To prevent and manage skin bacterial infections, consider the following steps:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly clean your skin, especially areas prone to sweating or friction.
- Keep Wounds Clean: Properly clean and cover any cuts, scrapes, or open wounds to prevent bacterial entry.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Avoid sharing towels, razors, clothing, and other personal items that could spread bacteria.
- Practice Insect Bite Prevention: Use insect repellent and protective clothing to minimize the risk of insect-borne infections.
- Prompt Treatment: If you suspect a bacterial infection, seek medical attention. Antibiotics or other treatments may be necessary.
- Vaccinations: Some bacterial skin infections, like impetigo, can be prevented through vaccination.
The symptoms and severity of a skin bacterial infection can vary widely. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, which may be topical or oral, depending on the infection’s extent and severity. It is important to note that infections should be evaluated by a Skin Specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
